APPENDIX
OUR TREATMENT
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
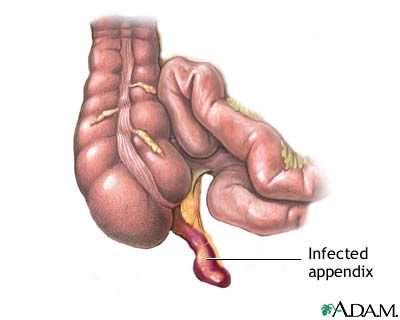
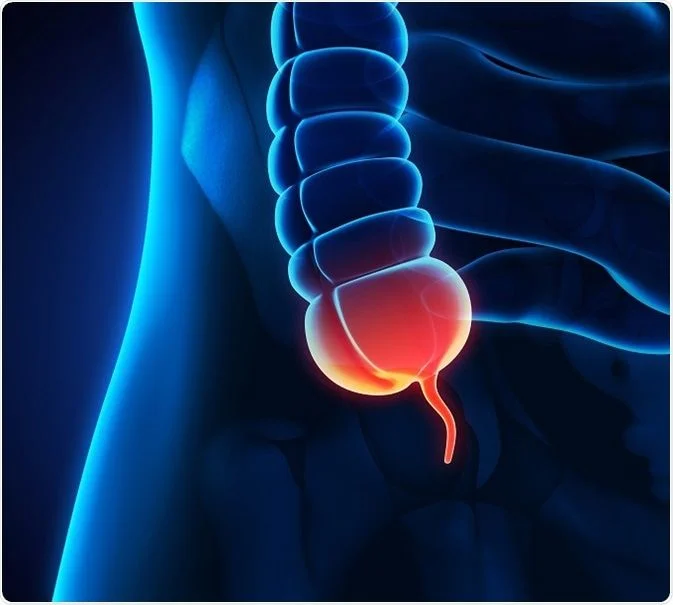
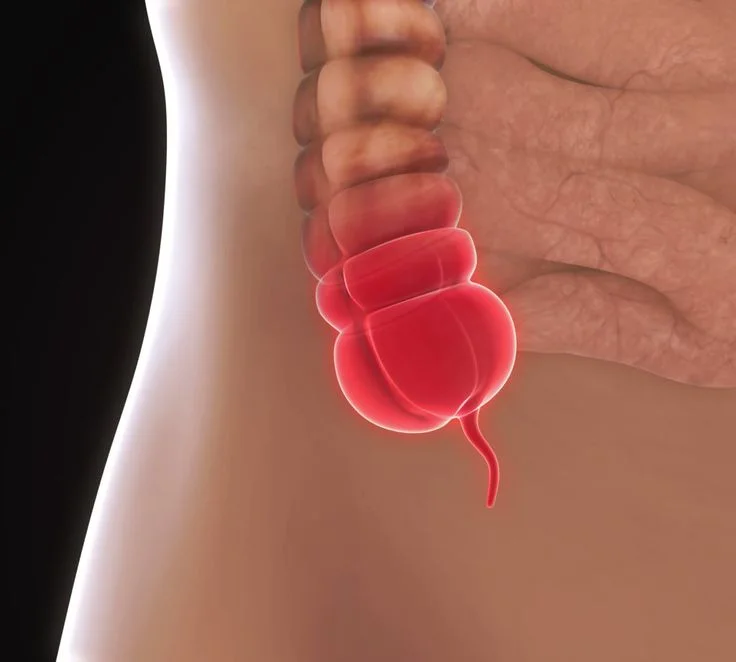
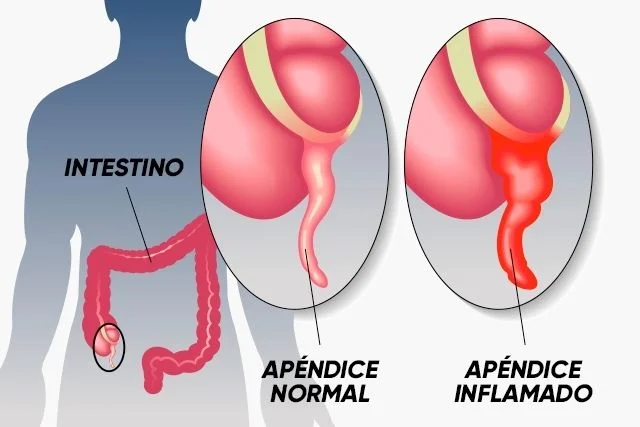
The appendix is a small thin finger-like pouch located on the right side of the abdomen as a small extension attached to the colon (Large intestine).
What is appendicitis?
When the appendix gets blocked or infected, it is called appendicitis. Appendix gets swollen and inflamed. When not treated, it gets ruptured and leads to situations that are life-threatening. A ruptured appendix spills all its content into the surrounding tissues or inflammation of the abdominal lining leading to peritonitis and sepsis, in turn leading to organ failure and death. This happens only if not treated in time.
What are the symptoms of Appendicitis?
The major symptom is a pain in the lower right-hand side of the abdomen. Other symptoms to look out for are – loss of appetite, pain around the belly & abdomen tenderness, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation or gas, Fever, pain in places like the back, or rectal area, indigestion, pain during urination. In children who are below 2 years, the parents need to look out for symptoms like vomiting, abdominal bloating, swelling, tender abdomen.
Types of Appendix Operation (Appendicitis Surgery)
- Open Appendectomy
This is one of the surgical procedures carried out in order to remove an appendix where the surgeon makes a single, large cut/incision of about 5-10 centimeters in the lower-right abdominal area. The appendix is completely removed, and the wound is closed using stitches.
symptoms
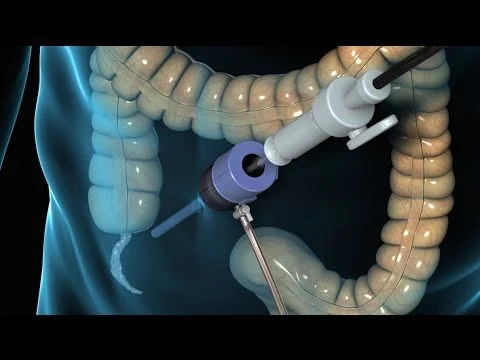
Laparoscopic
Laparoscopic Appendectomy
This is considered an advanced procedure compared to the conventional method of appendix removal surgery. In this method, the surgeon makes two or three tiny incisions in your abdomen rather than a single large cut and inserts a laparoscope – a thin tube with a camera and light attached to it, which allows them to view the inside of your abdomen. The appendix is tied and closed using sutures or surgical tape and covered with a dressing.
F.A.Q
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small, finger-shaped pouch that projects from the colon.
The most common symptoms of appendicitis are abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
Appendicitis is usually diagnosed based on a physical examination and a medical history. A doctor may also order blood tests and imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan.
The only way to treat appendicitis is to remove the appendix. This is usually done through surgery.
Age: 10-30 years old, family history, constipation.
Peritonitis: A serious infection of the lining of the abdomen.